Matter
Anything that occupies space and has mass is called Matter.
Physical Nature Of Matter
- Matter is made up of particles.
- The particles of matter are very small they are small beyond our imagination.
Characteristics Of Particles Of Matter
- Particles of matter have space between them.
- Particles of matter are continuously moving.
- Particles of matter attract each other.
States Of Matter
- There are three states of matter namely solid, liquid and gas.
- The main difference between these states of matter are given below:
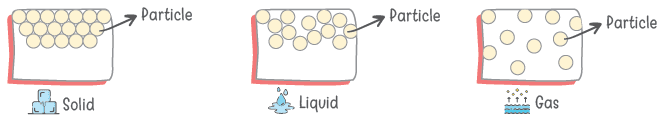

States Of Matter
| Solid | Liquid | Gas |
| Definite shape | No definite shape | No definite shape |
| Distinct boundaries and fixed volume | Fixed volume | No fixed volume |
| Not compressible | Can be compressible | Highly compressible |
| Cannot flow | Can flow | Can flow |
| Very less inter-particle space | Inter-particle spaces are more than in solids | Large inter-particle space is available |
| Maximum density | Density is between that of the solids and gases | Minimum density |
| Negligible rate of diffusion | Density is between that of the solids and gases | Maximum rate of diffusion |
| Inter-particle attraction is maximum | Rate of diffusion depends on inter-particle attraction | Inter-particle attraction is minimum |
| Inter-particle attraction is medium |
Effect Of Temperature
- The temperature at which a solid melts to become a liquid at the atmospheric pressure is called its melting point.
- The temperature at which a liquid starts boiling at the atmospheric pressure is known as its boiling point. Boiling is a bulk phenomenon.
- The phase change phenomenon where the substance is transformed form liquid state to solid state is known as freezing point.
- The phenomenon of changing of a liquid into its vapour state at any temperature below its boiling point is called evaporation. Evaporation is a surface phenomenon.
Factors affecting Evaporation
- An increase in surface area increases evaporation.
- An increase in temperature increases the rate of evaporation.
- A decrease in humidity increases the rate of evaporation.
- An increase in wind speed increases the rate of evaporation.
- Evaporation causes cooling effect.
- The change of the state of matter from the gas phase into liquid is known as condensation, it is reverse of evaporation.
- A change of state directly from solid to gas without changing into liquid state (or vice versa) is called sublimation.
- The phase change from the gaseous state to a solid state, without passing through the liquid state, is called deposition or re-sublimation.
Some Measurable Quantities and there Units
| Quantity | Unit | Symbol |
| Temperature | Kelvin | K |
| Length | Metre | m |
| Mass | Kilogram | Kg |
| Weight | Newton | N |
| Volume | Cubic metre | m3 |
| Density | Kilogram per cubic metre | Kg/m3 |
| Pressure | Pascal | Pa |

Comments are closed