Work
- When the force acts on an object or body and the object or body moves or shows displacement, then the force has done some work on the object or body.
- Mathematical formula: W = F × S or Work done = Force × Displacement
- If the displacement is zero, then work done will also be zero, W = 0.
- If work done is in the direction of force, then W = F × S.
- If work done is in the direction opposite to the force, then W = –F × S.
- Work done has only magnitude but no direction (scalar quantity)
- SI unit = Joule.
- 1 Joule = 1 Newton × 1 meter
- 1 Joule work is said to be done when 1 Newton force is applied on an object and it shows the displacemnt by 1 meter.
Energy
- Capacity of a body to do work.
- SI unit: Joule
Various Forms of Energy
| Potential Energy (PE) | Kinetic Energy |
| Energy possessed by an object by virtue of its position/configuration | Energy possessed by an object or body by virtue of its motion. |
| Gravitational potential Energy: Work done in raising an object from the ground to a point above the ground against gravity EP = mgh | KE (EK) =(1/2)mv2 |
| where m = mass of object | where m = mass of object or body |
| g = gravity | v = speed of object or body |
| h = height of object | KE of an object increases with its speed. |
| Unit: Joule |
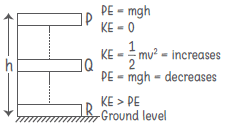
Law of Conservation of Energy
Energy can neither be created nor be destroyed, it can only be transformed from one form to another.
- Sum of the kinetic and potential energies of an object is called its mechanical energy.
Total Energy (Before transformation) = Total Energy (After transformation)

Commercial Unit of Energy
- Kilowatt hour (KWh)
- Energy used in 1 hour at the rate of 1KW is called 1KWh
- 1 KWh = 3.6 × 106 J
- 1 Unit = 1 KWh
Power
- Rate of doing work
- Power =(Work/Time) ∴ P =(W/T)
- SI Unit = Watt =(Joules/Second) ⇒ 1 Kilowatt = 1000 Watts; 1 Kilowatt = 1000 J/s


Comments are closed